Grep is not really the right tool for the job here, but a quick look at the grep manpage should help (please note that grep will vary semi-wildly between distributions, as some may use GNU by default and others may use something else).
I clearly remember my first interaction with Linux. I was a technical trainer at the time. My experience, courses, and certifications revolved around Mac OS X and Windows Server. The company owner sent an email to the entire training department asking for someone to begin investigating Linux. I was the only trainer that stepped forward. A few weeks later, I was attempting to get a Linux distribution installed on one of the computers in the back of my classroom. These were the days of the 'smoke error' if you got the monitor's vertical refresh rate wrong, etc. It took me several attempts to complete the installation, but finally, the machine booted, I signed in with my name and password, and the bash prompt flashed at me.
Mac OS X is a powerful Unix OS enabling the users to use many Unix tools such as grep, awk, sed, etc.Unfortunately, these are generally command line tools, not very well integrated with the GUI environment. TextMate for Mac. Textmate is a versatile plain text editor with a unique and innovative.
And I knew no commands.
More Linux resources
Sometimes those that are new to Linux just need a few things to get them started. We all had to learn basic commands such as ls, ifconfig, hostname, cd, chmod, and so forth. However, the next step comes in knowing the commands that will make a practical difference in your sysadmin life. I've collected several of my favorite commands below. Most of these are very fundamental commands, but using them effectively keeps me efficient.
Restart services

We all know it—if you change a configuration file, you must restart the service so that it becomes aware of the change. These days, we typically use systemctl to manage services, but I've also included the older service command below:
Storage space
Storage space seems to be an eternal struggle for admins. There are two different but related commands that can help you understand your storage utilization: du and df. I always add the -h option to them both. Doing so displays the storage capacity output in a 'human-friendly' way (such as GBs or TBs).
Ping for device reboot status
Often, when updating servers, applying security patches, or installing software, the device must be rebooted for the configuration to continue. If you're in the habit of managing your servers remotely (and you should be!), it can be difficult to tell when a server has completed its reboot and is ready for you to reestablish an SSH connection. This is a great opportunity to use ping. We usually rely on ping as a troubleshooting tool to confirm or deny whether a remote host is available. This is the same idea, but you're using it to inform you when a remote host begins responding to ping requests again (and therefore has completed its reboot).
Note: You can use this trick with Windows by running a continuous ping: ping -t 10.1.0.11
[ You might also like: 10 basic Linux commands you need to know ]
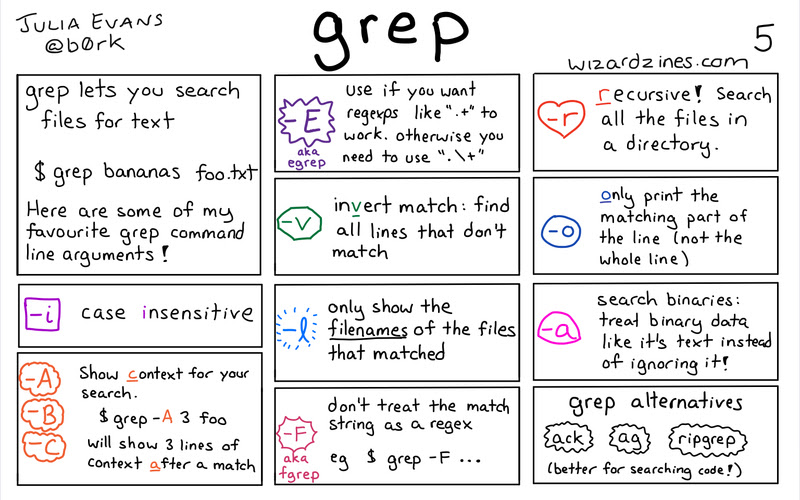
Use grep with other commands
Of course, grep is an incredibly handy utility. One of the best ways to use grep is in conjunction with other commands, such as ls or ps. By piping the output of these commands into grep, you can easily display the information you need. Use the -i option to ignore case when matching a string.
Display the network around you
Displaying the devices available on the network around you is helpful for troubleshooting or understanding server roles. The nmap utility is incredibly powerful, with a great many options. However, even a basic nmap scan is useful and not difficult to remember. Here are a few examples.
A scan of your computer to learn about network services and ports:
A basic ping scan to identify the surrounding hosts:
A basic scan to identify a specific host:
Append information
The following redirection operator is incredibly helpful. While you can use the single > character to redirect the output of a command to a file, the >> operator appends the output to any data that might already exist in the file. The redirect operator (>) overwrites any existing content.
Notice that I have begun some basic system documentation using commands we already viewed in the three command examples above.
Note: Over the years, I have recommended to students that they don't even bother to use the > basic redirector at all. The >> append redirector is safer, and works fine even if the destination file is empty.
Other results to append:
View information with cat and tail

The cat command displays the contents of a file. Whether it be configuration files, logs, or user documents, sysadmins spend a lot of time viewing file contents. The cat command is great for this.
Don't forget to use | less to break long output into manageable pages:
Another excellent command for displaying information is tail. It displays the last lines of a file. Most of us use tail when viewing log files because the most recent log entries will be at the bottom of the file.
Don't forget the related head command, which displays the top of a file.
[ Get this free ebook: Managing your Kubernetes clusters for dummies. ]
Vim tips
Best Grep Tool For Os X Download
In this next section, I freely admit that I'm going to cheat. Up to this point, I have shown one or maybe two related commands per section. This section covers Vim (which is arguably one of my favorite commands). More specifically, however, I show several tricks inside Vim that make my life easier.
Use the Esc key
Vim can be confusing to new Linux users. One secret of success that I pass on to my students when introducing Vim is this: If you're ever confused about which of the Vim modes you're in (Command, Execute, Insert), press the Esc key several times. That gets you back to the 'home base' of Command mode. From there, you can use : for Execute mode or i for Insert mode.
Display line numbers
You can cause Vim to display line numbers by using the following Execute mode command:
Line numbers now appear along the left side of the file. You can make this setting permanent by editing the ~/.vimrc file.
There are many other configurations you can set, including syntax checking and highlighting the current line. Visit the Vim documentation for ideas.
Jump to the bottom, top, or specific line of a file
Many configuration files are long, and you may need to use Vim to enter content at the bottom of the file. The uppercase G key in Command mode jumps you to the end of the file. Typing gg jumps you to the top of the file. These two navigation tricks can save you a lot of time.
You can also jump to a specific line number in a file. Do so by typing 42G in Command mode to jump to line 42. This is a great example of when the :set number value discussed above helps.
Keyword searches
You can keyword search in Vim by using a forward slash (/) and then typing the desired string. Do this while in Command mode.
Best Grep Tool For Os X Operating System
The above example searches for the string hosts in the file. Use n and N to jump to instances of the string.
Note: Here is a great article from Ricardo Gerardi on How to use Ansible to configure Vim.
Best Grep Tool For Os X Catalina
Wrap up
Best Grep Tool For Os X Os
This is certainly not an exhaustive list of useful Linux commands. The list does, however, represent tips and tricks that I've found helpful over the years. Many sysadmins have contributed ideas, useful commands, and creative ways of using Linux functionality to Enable Sysadmin, so be sure to look for more articles that will make you more efficient.